Table Of Content
When a third variable is involved and has not been controlled for, the relation is said to be a zero order relationship. In most practical applications of experimental research designs there are several causes (X1, X2, X3). In most designs, only one of these causes is manipulated at a time.
Why Quality by Design (QbD) is vital for pharmaceutical R&D
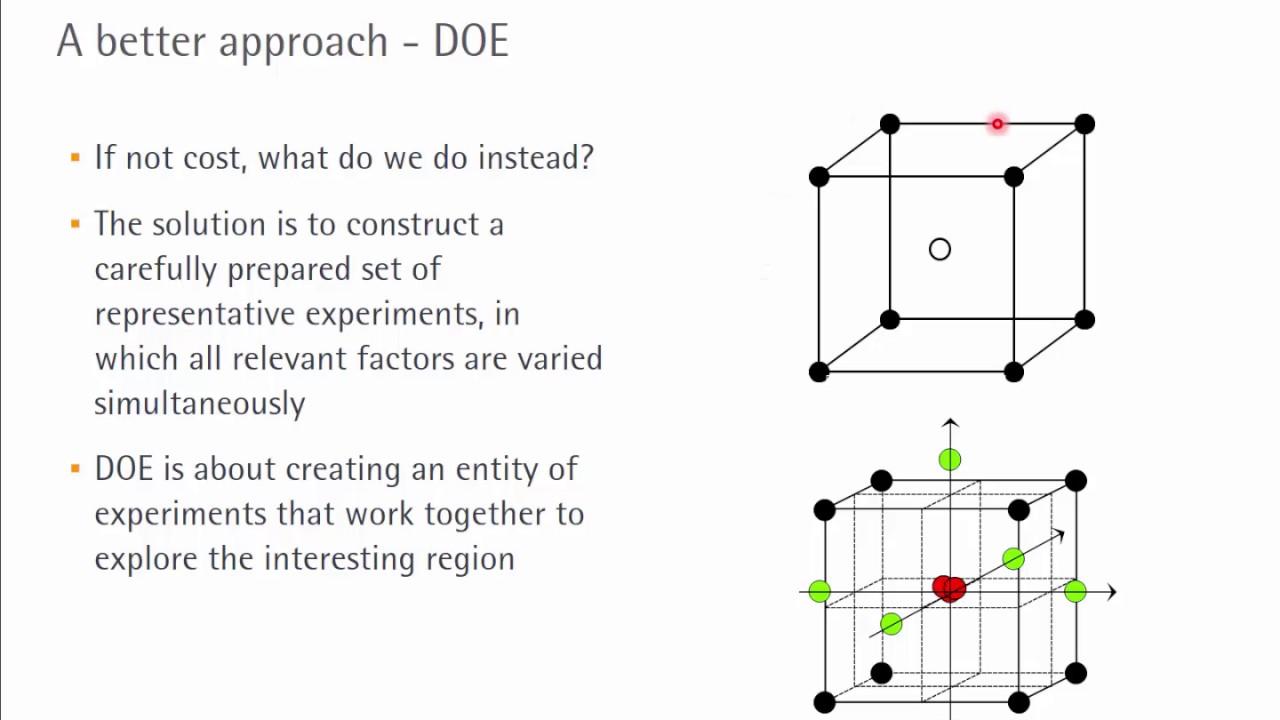
It is limited in both the number of variables that you can investigate and, critically, it precludes any investigation of how variables interact. Most biological processes are complicated, complex, and multidimensional.7 So, changing one factor probably changes something else. The statistician Ronald Fisher, who attended the tea party, devised an experiment to test her claim. The lady was randomly given four cups in which tea was poured before the milk and four where the milk was poured first. They enlisted the company’s Master Black Belt to help them do the experiment using a two-level approach. In this course we will pretty much cover the textbook - all of the concepts and designs included.
Statistical control
His methods were successfully applied and adopted by Japanese and Indian industries and subsequently were also embraced by US industry albeit with some reservations. It is best that a process be in reasonable statistical control prior to conducting designed experiments. Investigators should ensure that uncontrolled influences (e.g., source credibility perception) do not skew the findings of the study. Manipulation checks allow investigators to isolate the chief variables to strengthen support that these variables are operating as planned. Overall, the purpose of experimental design is to provide a rigorous, systematic, and scientific method for testing hypotheses and establishing cause-and-effect relationships between variables.
Overview: What is DOE?
Only when this is done is it possible to certify with high probability that the reason for the differences in the outcome variables are caused by the different conditions. Therefore, researchers should choose the experimental design over other design types whenever possible. However, the nature of the independent variable does not always allow for manipulation. In those cases, researchers must be aware of not certifying about causal attribution when their design doesn't allow for it. The same goes for studies with correlational design (Adér & Mellenbergh, 2008).
Step 2: Write your hypothesis
Create your experimental design with a simple Python command by Tirthajyoti Sarkar - Towards Data Science
Create your experimental design with a simple Python command by Tirthajyoti Sarkar.
Posted: Wed, 04 Jul 2018 02:31:34 GMT [source]
This is a brute force technique that you can get by with when you have just a few variables or interactions. The downside is that with large variable (factor) sets, you will spend a lot of resources doing this. You may miss the complicated interactions other more sophisticated designed experiments will give you. Sometimes randomisation isn’t practical or ethical, so researchers create partially-random or even non-random designs.
Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples
Often doing a full factorial design analysis is impossible or impractical. Here’s how you can optimize your resources and still achieve a rigorously-supported decision. Next, we must understand the factors that can affect an outcome to create the appropriate design to determine how to structure our experiment. In your research design, it’s important to identify potential confounding variables and plan how you will reduce their impact. Experimental designs are a set of procedures that you plan in order to examine the relationship between variables that interest you. You should also include a control group, which receives no treatment.

Note that the tool is called Design of Experiments, plural; a single experiment, even with multiple factors, will not provide enough data. One experiment may provide results which indicate a different problem to solve thus requiring the design of additional experimentation. In the planning stage, enough time needs to be included in the overall project timeline to plan, execute, evaluate, and document the Design of Experiments.
After viewing them, the customer then ranked the different mockups from most preferred to least preferred. To keep matters simple, they went with a quarter fraction design, or 16 different mockups. Otherwise, you’re asking customers to try and differentiate their preference and rank way too many options. If you have a treatment group and a control group then, in this case, you probably only have one factor with two levels. A more effective and efficient approach to experimentation is to use statistically designed experiments (DOE).
Once you’ve identified the best potential factors, you can do a full factorial with the reduced number of factors. DOE statistical outputs will indicate whether your main effects and interactions are statistically significant or not. You will need to understand that so you focus on those variables that have real impact on your process. The randomised block design is preferred in the case when the researcher is clear about the distinct difference among the group of objects.
Use arrows to show the possible relationships between variables and include signs to show the expected direction of the relationships. Then you need to think about possible extraneous and confounding variables and consider how you might control them in your experiment. DOE helps reduce the time, materials, and experiments needed to yield a given amount of information compared with OFAT.
For example, it isn't possible to fully understand the functional consequences of changing a protein's structure without understanding all the contexts in which it appears. Its interactions within biological networks are what really define its function, so even minor changes can produce a plethora of unpredictable down- and upstream effects. In a series of blogs, we’re going to explore the basis of DOE, who should consider DOE, and some ways in which this methodology helps experimental biologists deal with life’s inherent complexity. Once they gathered all the data and analyzed it, they concluded that menu orientation and loading speed were the most significant factors. This allowed them to do what they wanted with font, primary graphic, and color scheme since they were not significant. Specify how you can manipulate the factor and hold all other conditions fixed, to insure that these extraneous conditions aren't influencing the response you plan to measure.
You will need to control those to reduce the noise and contamination that might occur (which would reduce the value of your DOE). In a conjoint analysis DOE, you would create mockups of the various combinations of variables. A sample of customers were selected and shown the different mockups.
Next, we evaluate what will happen when we fix the volume at 550 ml (the optimal level) and start to change the second factor. In this second experimental series, the pH is changed from 2.5 to 5.0 and you can see the measured yields. We change the experimental factors and measure the response outcome, which in this case, is the yield of the desired product. Using the COST approach, we can vary just one of the factors at time to see what affect it has on the yield. The key difference between observational studies and experiments is that, done correctly, an observational study will never influence the responses or behaviours of participants.
So, the researcher will design the experiments for the purpose of improvement of precision. It is called experimental design or the design of experiments(DOE). In this article, let us discuss the definition and example of experimental design in detail. Project Managers use the Design of Experiment tool in the Quality Planning process to determine the factors of a process, the way to test those factors, and what impact each has on the overall deliverable. Project Managers and those preparing for the Project Management Professional (PMP®) certification need to know of the DOE regardless of the industry in which they work. A design of experiments (DOE) is a set of statistical tools for planning, executing, analyzing, and interpreting experimental tests to determine the impact of your process factors on the outcomes of your process.
However, because field experiments are not as controlled as laboratory experiments, they may be subject to more sources of error. This design involves grouping participants within larger units, such as schools or households, and then randomly assigning these units to different treatment groups. In this design, participants are randomly assigned to one of two or more groups, and each group is exposed to a different treatment or condition. Plus, we will we have support for different types of regression models.

No comments:
Post a Comment